Our everyday lives depend heavily on technology, yet it frequently comes with a language that can be daunting or complicated. Many people are left perplexed when terms like “cloud computing,” “firewall,” or “API” are used in talks. This tutorial can help you if you’ve ever been overwhelmed by technical jargon. Let’s simplify some frequently used IT phrases so that everyone may comprehend them.
1. An Introduction to IT Jargon
Technologies that process, store, and transfer data are collectively referred to as information technology, or IT. From hardware and software to networking and cybersecurity, this wide field covers a variety of ideas. We’ll go over some frequently used terminology you’ll probably come across below and provide clear definitions.
2. Software Vs Hardware
Hardware: Things you can physically touch, such as your printer, laptop, or smartphone. Hardware can be thought of as a computer system’s body.
Software: Operating systems and applications that operate on hardware, such as mobile apps, Windows, and macOS. The brain that instructs hardware is called software.
Comparatively speaking, the software is the driver and navigation system, and the hardware is the engine, wheels, and body of your computer.

3. The Cloud
The phrase “cloud” describes servers that may be accessed online, together with the databases and applications that operate on them. You can access your data from any location with an internet connection by saving it in “the cloud” as opposed to on your computer’s hard disc.
For instance, cloud-based storage options include Dropbox, iCloud, and Google Drive.
Why it matters: Because files and apps are available everywhere, cloud computing facilitates distant work and collaboration.
4. A firewall
Incoming and outgoing network traffic is monitored and managed by a firewall, a type of digital security system. In order to defend against online dangers, it serves as a virtual gatekeeper, determining which data should be blocked and which should flow through.
For instance, your home Wi-Fi router’s firewall keeps unwanted users from accessing your devices.
Why it matters: It’s a vital tool for preserving security and privacy in both private and professional contexts.
5. Application Programming Interface (API)
A set of guidelines known as an API makes it possible for various software applications to speak with one another. Imagine it as a translator that facilitates data sharing and communication between two apps.
For instance, a weather app on your phone might use an API to retrieve and show weather information from a server.
Why it matters: APIs allow for smooth service integration, such as integrating a task management tool with your calendar.
6. Domain Name System (DNS)
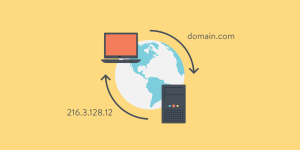
In order for computers to find one another on the internet, DNS converts human-readable website names (such as www.google.com) into IP addresses (such as 192.168.1.1).
Analogy: Consider DNS to be the internet’s equivalent of a phone book, connecting names to numbers.
Why it matters: In the absence of DNS, accessing websites would require you to memorize lengthy strings of digits.
7. Bandwidth
The maximum quantity of data that may be sent across an internet connection in a specific amount of time is referred to as bandwidth. Usually, megabits per second (Mbps) are used to measure it.
Comparing bandwidth to a highway’s width, more cars (data) can move through it at once the broader the highway.
Why it matters: More bandwidth guarantees faster downloads, more fluid streaming, and improved internet performance in general.
8. Virtual Private Network, or VPN
By establishing a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet, a virtual private network (VPN) conceals your location and online activities.
For instance, you can safely browse the web on public Wi-Fi networks or access content that is blocked in your country by using a VPN.
Why it matters: It protects sensitive data from hackers and improves internet privacy.
9. Malware
Malware is software that is intended to damage, take advantage of, or compromise your device or data in some other way. Spyware, ransomware, and infections are common forms.
Example: Malware may infect your computer if you click on a dubious email link.
Why it matters: Protecting personal and corporate data requires an understanding of how to identify and steer clear of malware.
10. Machine learning and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the term for technology that simulates human intelligence in order to carry out tasks like decision-making and problem-solving.
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence in which systems learn from their experiences and get better without explicit programming.
For instance, machine learning enables Netflix to suggest shows based on your viewing preferences, while artificial intelligence powers virtual assistants like Siri.
Why it matters: These technologies are transforming a variety of industries, including finance and healthcare.
11. Cookies
Cookies are little files that websites save on your computer in order to remember your browsing history, login credentials, and preferences.
For instance, cookies remember your selections when you add products to an online shopping basket and return to the website later.
Why it matters: Being aware of cookies enables you to maximise your browsing experience and control your online privacy.

12. Open Source
Software that has its source code made freely accessible for anyone to read, alter, and distribute is referred to as open source.
For instance, because the Linux operating system is open source, developers from all over the world are welcome to contribute to its advancement.
Why it matters: Open source software is more affordable than proprietary software and encourages creativity and teamwork.
13. The use of encryption
The process of turning data into a code to stop unwanted access is called encryption.
For instance, encryption is used by messaging apps and online banking to protect your data.
Why it matters: It is essential to contemporary cybersecurity, safeguarding private information such as financial transactions and passwords.
14. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects that are linked to the internet and have the ability to gather and exchange data.
For instance, the Internet of Things ecosystem includes connected cars, fitness trackers, and smart thermostats.
Why it matters: Although IoT makes ordinary chores easier, it also raises security and privacy concerns.
In conclusion,
Tech jargon doesn’t have to be difficult to understand. You can traverse the digital world with confidence if you can deconstruct complicated jargon into understandable, straightforward explanations. Being knowledgeable will enable you to make wiser choices as technology develops further, whether it’s selecting a new gadget, safeguarding your online privacy, or investigating fascinating new developments.
Are you prepared to go further? You’ll quickly become fluent in the language of IT if you begin putting some of the aforementioned ideas into practice. Talk to us about Balliante Education and our workshops on Microsoft products such as Word, Outlook, Excel etc.